How Does the Hydraulic Pump Work?
In modern construction machinery, hydraulic working devices are basically inseparable. Even if the main working devices do not use hydraulic equipment, hydraulic systems are usually needed to achieve some auxiliary work. Hydraulic is so important, and it is very close to our life and work. For example, a torque wrench needs to use a hydraulic pump to provide power, and a bolt tensioner also needs a hydraulic pump as a source of driving force.
But it’s still mysterious for ordinary people who are not professional, and various principles of it are not well understood. They may know the word, but don’t know others.
When it comes to hydraulic systems, it is necessary to talk about the most important part-pump. The pump is the foundation of the hydraulic system. The main function of the pump is to transport or pressurize the liquid.
The birth of the pump was very early. The equipment used to lift water in ancient times was the earliest pump, such as the waterwheel in China and the chain pump in Egypt.
After the industrial revolution, with the widespread use of steam engines, the demand for large flow and high-speed liquids increased, and mechanical pumps began to be born. Nowadays, pumps have become more and more widely used in all walks of life, and there are more and more types of pumps. The pump plays an important role as a power equipment.
Hydraulic transmission is widely used in various fields and is called the “muscle of industry”. In hydraulic transmission, the hydraulic pump is the power element and the “source” of its strength. Especially in the era of mechanization, it is everywhere. Its importance is self-evident.
Complete hydraulic system composition
A complete hydraulic system consists of five parts, namely power components, executive components, control components, auxiliary components and hydraulic oil.
The function of the executive components (hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors) is to convert the pressure energy of the liquid into mechanical energy, and drive the machinery to perform linear reciprocating or rotary motion.
Control components (various hydraulic valves) control and regulate the pressure, flow and direction of the liquid in the hydraulic system.
Auxiliary components include fuel tanks, oil filters, sealing rings, pressure gauges, etc. Hydraulic oil is the energy transfer medium in the hydraulic system, including mineral oil and synthetic hydraulic oil.
A hydraulic pump is a kind of power element that provides liquid pressurization for hydraulic transmission. It is a kind of pump and an energy conversion device. Its function is to convert the mechanical energy of the power machine driving it (such as an electric motor or an internal combustion engine) into a transmission The hydraulic pressure energy into the system is similar to the function of a pump.
According to the structure, hydraulic pumps can be divided into three types: gear pumps, vane pumps and plunger pumps.
Gear pump
The gear pump has the characteristics of small size, simple structure, strong anti-pollution, low price, large leakage, large noise, large flow pulsation, and unadjustable displacement.
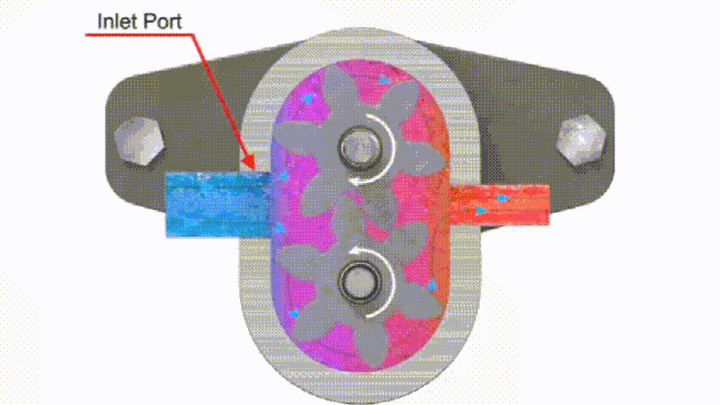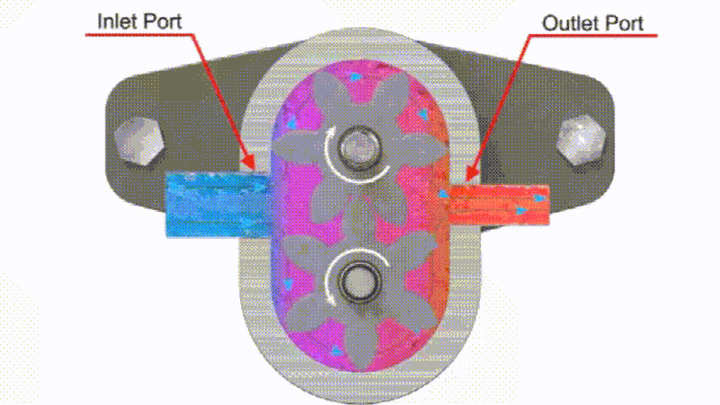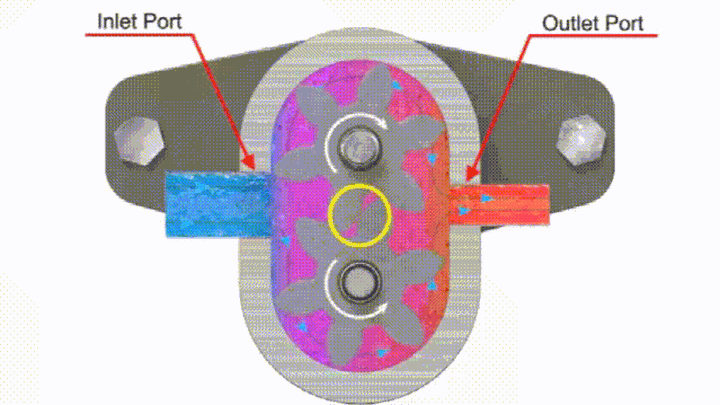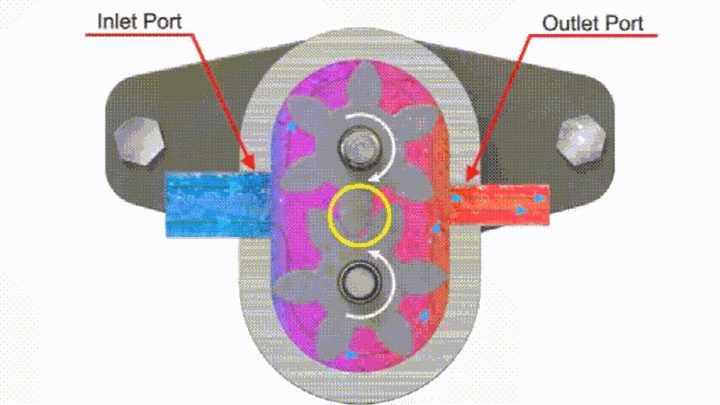

The gear pump is made up of two gears meshing with each other. When a motor or engine drives one of the gears, the other gear that meshes with it will rotate at the same time. The pair of gears rotate with each other, and the teeth on the side of the meshing teeth are gradually disengaged. The volume of the sealed cavity increases, forming a partial vacuum. The hydraulic oil in the oil tank is sucked in under the action of atmospheric pressure to fill the increasing volume. The sucked-in hydraulic oil fills up the tooth groove, and as the tooth groove rotates, it brings the oil to the pressure oil cavity on the other side of the meshing area. The two gear meshing lines separate the oil suction chamber and the oil pressure chamber, so that no hydraulic oil leakage occurs between the oil suction area and the oil pressure area, and the gears continuously rotate to complete the oil suction and pressure oil process again and again.
There is also a gear pump called an internal gear pump, which is also used in hydraulic equipment. This kind of pump has a pair of gears that mesh with each other to form an eccentric structure, in which the teeth of the internal gear extend outward and are driven by a motor, and the teeth of the external gear meshed with it extend toward the center of the pump. When the pinion gear rotates, it drives the external gear that meshes with it to rotate. The gear on the side of the oil suction port exits meshing, and the volume increases, forming a partial vacuum to suck oil. The gear on the side of the oil pressure port enters the meshing volume to reduce and press oil. The crescent plate in the pump body separates the oil suction area from the oil pressure area.
Vane pump
The vane pump has the characteristics of uniform flow, stable operation, low noise, high working pressure and volumetric efficiency, and complex structure.
The vane pump is an eccentric structure formed by the rotor and the vanes. As the rotor rotates under the drive of the drive shaft, the lower end of the blade always maintains sufficient pressure due to the action of spring or hydraulic oil, so that the top end of the blade can be close to the inner wall of the pump. During the rotation, any two adjacent blades and the pump body enclose a closed space. When the closed space gradually becomes larger, the hydraulic oil is sucked into it. When the volume of the closed space becomes smaller, the hydraulic oil inside The hydraulic zone is pressed out.
Plunger pump
Plunger pumps have high volumetric efficiency, low leakage, and can work under high pressure. They are mostly used in high-power hydraulic systems, but they are complex in structure, require high material and processing accuracy, are expensive, and require high oil cleanliness.
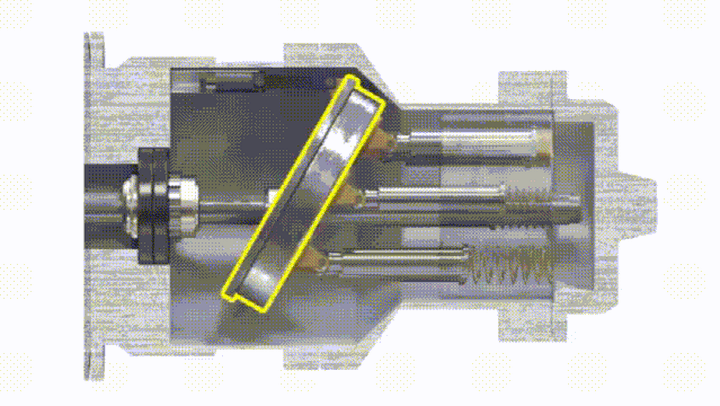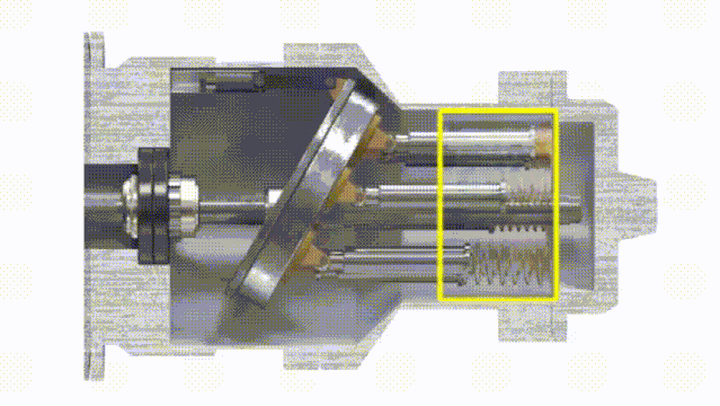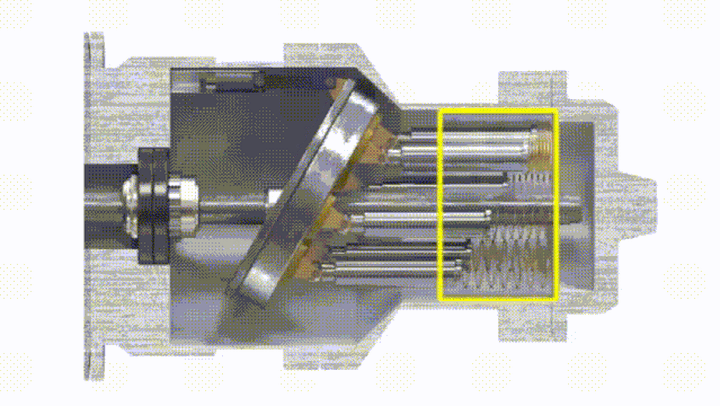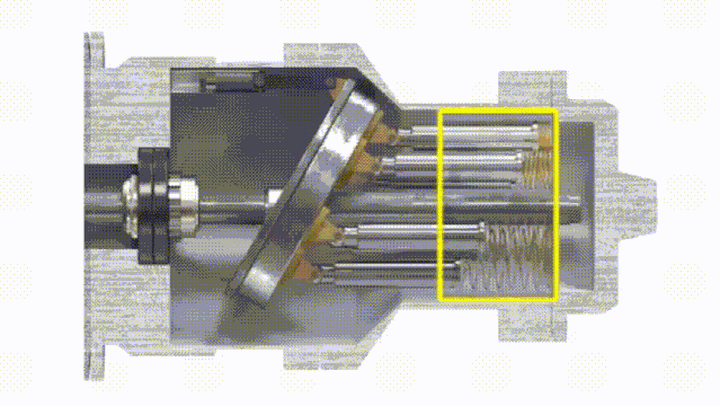

The plunger pump has a drive shaft connected with the cylinder body. The plungers are evenly distributed in the cylinder body along the circumference. One end of the plunger is pressed against a fixed swash plate, and a compression spring is installed between the other end and the bottom surface of the pump body. . The swash plate has an inclination angle relative to the axis of the pump body, and the piston will always press on the swash plate.
The sealing volume around the piston and the cylinder on one side of the cylinder gradually increases into an oil suction zone, and the other side is gradually reduced to a pressure zone due to the surrounding sealing volume.
Taking a single plunger as an example, when the cylinder rotation angle is 0° to 180°, the plunger gradually extends, and the sealing working volume of the cylinder hole at the bottom of the plunger increases. This process sucks oil. When the rotation angle is between 180° and 360°, the volume of the cylinder bore decreases, and the oil is pressed during this process. The greater the inclination angle of the swash plate, the greater the difference in the volume of the cylinder bore at the bottom of the piston, and the greater the displacement of the pump. The displacement of the swash plate plunger pump can also be changed by adjusting the tilt angle of the swash plate.
Summarize
Hydraulic pumps are key components of various equipment, and their performance and service life determine to a large extent the working capacity of the entire hydraulic system. With the advancement of technology, the performance of hydraulic pumps is becoming more and more perfect, and they are widely used in industrial equipment and various fields. TorcStark has extensive experience in the production of hydraulic torque pumps and bolt extensioner pumps. It is one of the world’s well-known manufacturers. Welcome to contact us to know more about hydraulic pumps.