
In today’s blog post we want to introduce non-threaded mechanical fasteners, obviously made of stainless steel.
What are these fasteners? And how to use them?
What are the non-threaded mechanical fasteners?
There are different types of fasteners. For example, the main are
- Feather keys
- Parallel keys
- Pins
- Retaining rings
- Groove profiles.
#inbound-list.class-ORJPfqwjzF li {
color:#000000;
list-style: none;
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 16px;
vertical-align: top;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#inbound-list.class-ORJPfqwjzF li:before {
background: transparent;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50%;
color:#0080ff;
display: inline-block;
font-family: ‘FontAwesome’;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 18px;
margin-right: 0.5em;
margin-top: 0;
text-align: center;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 580px) {
#inbound-list.class-ORJPfqwjzF li {
width:100%;
}
}
p:empty {
display:none;
}
How to use them?
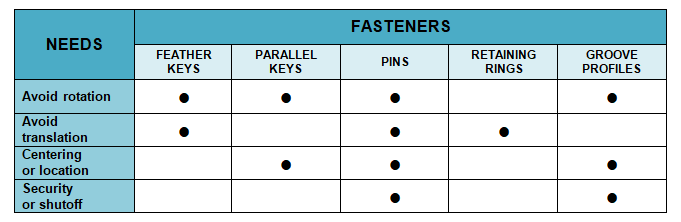
Match two (or more) elements, which means preparing connections making them integral. But how can we make it? It is necessary to introduce some constraints that (partially or wholly) are able to prevent the relative movements of the coupled parts. Then, this type of mechanical connections allow to satisfy different needs. But which ones?
- Avoid mutual rotation (e.g. feather keys, parallel keys, pins and groove profiles)
- Avoid mutual translation (e.g. feather keys, pins, retaining rings)
- Ensure a centering or a location (e.g. parallel keys, pins, retaining rings)
- Providing security against spontaneous disassembly (e.g. pins and retaining rings)
- Prevent moving over a defined limit (e.g. pins and retaining rings).
#inbound-list.class-HZnbzNKjYD li {
color:#000000;
list-style: none;
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 16px;
vertical-align: top;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#inbound-list.class-HZnbzNKjYD li:before {
background: transparent;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50%;
color:#0080ff;
display: inline-block;
font-family: ‘FontAwesome’;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 18px;
margin-right: 0.5em;
margin-top: 0;
text-align: center;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 580px) {
#inbound-list.class-HZnbzNKjYD li {
width:100%;
}
}
p:empty {
display:none;
}
Below, a summary diagram.
Here are a few examples of non-threaded mechanical fasteners.
PARALLEL KEYS
The parallel key has a square or rectangular cross-section. It is a prism-shaped fasteners and this is similar to feather keys but with all parallel faces. For example, we can find different types of parallel keys as:
- B form
- A form
- C form.
#inbound-list.class-jdEqfVUOaS li {
color:#000000;
list-style: none;
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 16px;
vertical-align: top;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#inbound-list.class-jdEqfVUOaS li:before {
background: transparent;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50%;
color:#0080ff;
display: inline-block;
font-family: ‘FontAwesome’;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 18px;
margin-right: 0.5em;
margin-top: 0;
text-align: center;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 580px) {
#inbound-list.class-jdEqfVUOaS li {
width:100%;
}
}
p:empty {
display:none;
}
PINS
The pin is a cylindrical element with positioning, locking or connection functions. The pins can be categorized by their different shapes. For example:
- Straight pin
- Taper pin
- Spiral wrapped pin
- Grooved pin.
#inbound-list.class-JjUmSMgifL li {
color:#000000;
list-style: none;
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 16px;
vertical-align: top;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#inbound-list.class-JjUmSMgifL li:before {
background: transparent;
border-radius: 50% 50% 50% 50%;
color:#0080ff;
display: inline-block;
font-family: ‘FontAwesome’;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 18px;
margin-right: 0.5em;
margin-top: 0;
text-align: center;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 580px) {
#inbound-list.class-JjUmSMgifL li {
width:100%;
}
}
p:empty {
display:none;
}
RETAINING RINGS
The retaining rings (also known as “SEEGER“) are unified mechanical fasteners to use for shafts and for bores. In fact, these are to axially secure bearings, shafts and piston pins, which will eliminate the fixed problem long shafts and bores. What are made the rings? Generally with the AISI420 martensitic steel. In the presence of a shaft, locating rings are placed in a fitted external locations. Contrarily, in the presence of bores (or grooves) these rings are placed in internal locations, the latter made by turning operations.
Visit our website www.inoxmare.com and check out our stainless steel mechanical connections. Sign in on our web shop and you can see real-time availabilities and prices.
Visit website
Do you want to read more article? Learn more.
a.mt-share-inline-bar-sm img {
width: 34px;
height: auto;
border: 0px;
}
.inbound-social-share-bar-container {
display: inline-block;
}
.inbound-social-share-header {
vertical-align: middle;
}
a.mt-share-inline-bar-sm:hover {
z-index: 50;
-webkit-transform: scale3d(1.075, 1.075, 1.075);
}
a.mt-share-inline-bar-sm {
display: inline-block;
width: 64px;
height: 32px;
border-top-left-radius: 0px;
border-top-right-radius: 0px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 0px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 0px;
margin-right: 0px;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
transition: all 100ms ease-in;
-webkit-transition: all 100ms ease-in;
-webkit-transform: scale3d(1, 1, 1);
}
a.mt-share-inline-circle-sm img {
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border: 0px;
}
a.mt-share-inline-circle-sm {
display: inline-block;
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border-top-left-radius: 50%;
border-top-right-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-right-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-left-radius: 50%;
margin-right: 4px;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-sm img {
width: 34px;
height: auto;
border: 0px;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-sm {
display: inline-block;
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border-top-left-radius: 2px;
border-top-right-radius: 2px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 2px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 2px;
margin-right: 4px;}
.mt-google:hover {
background-color: rgb(225, 95, 79);
}
.mt-google {
background-color: rgb(221, 75, 57);
}
.mt-linkedin:hover {
background-color: rgb(16, 135, 192);
}
.mt-linkedin {
background-color: rgb(14, 118, 168);
}
.mt-twitter:hover {
background-color: rgb(8, 187, 255);
}
.mt-twitter {
background-color: rgb(0, 172, 238);
}
.mt-facebook:hover {
background-color: rgb(66, 100, 170);
}
.mt-facebook {
background-color: rgb(59, 89, 152);
}
.mt-pinterest:hover {
background-color: rgb(221, 42, 48);
}
.mt-pinterest {
background-color: rgb(204, 33, 39);
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm img {
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm.mt-google:hover {
background-color: rgb(221, 75, 57) !important;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm.mt-linkedin:hover {
background-color: rgb(14, 118, 168) !important;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm.mt-twitter:hover {
background-color: rgb(0, 172, 238) !important;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm.mt-facebook:hover {
background-color: rgb(59, 89, 152) !important;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm.mt-pinterest:hover{
background-color: #dd2a30 !important;
}
a.mt-share-inline-square-bw-sm {
display: inline-block;
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border-top-left-radius: 2px;
border-top-right-radius: 2px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 2px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 2px;
margin-right: 4px;
text-align: center;
background-color: rgb(51, 51, 51);
transition: background-color 300ms ease-in;
-webkit-transition: background-color 300ms ease-in;
}




